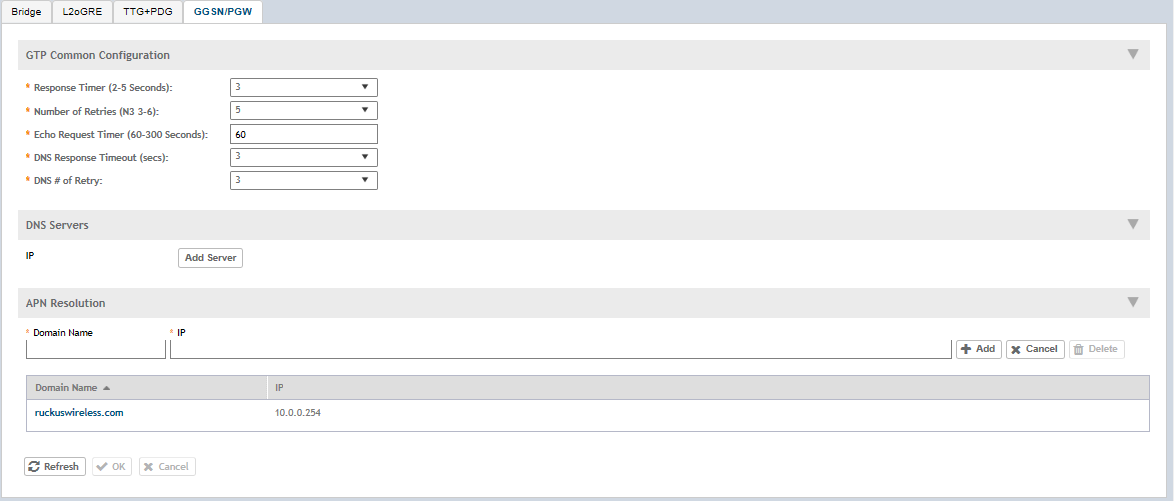
Configuring the GGSN/PGW Service
GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) transmits user data packets and signaling between controller and GGSN. GTP encapsulates traffic and creates GTP tunnels, which act as virtual data channels for transmission of packet data between controller and GGSN. A GTP tunnel is established between controller and GGSN for a data session initiated from UE.
A GTP tunnel is identified by a pair of IP addresses and a pair of GTP Tunnel End Point Identifiers (TEIDs), where one IP address and TEID is for the SGSN and the other is for GGSN. TEID is a session identifier used by GTP protocol entities in SGSN and GGSN.
GTP separates signaling from payload. Traffic is sorted onto a control plane (GTP-C) for signaling and a user plane (GTP-U) for user data. GTP-C is a tunnel control and management protocol and is used to create, modify and delete tunnels. GTP-U is a tunneling mechanism that provides a service for carrying user data packets.
To configuring the GGSN/PGW Service: