Troubleshooting Client Connections
This feature allows network administrators to connect to client devices and analyze network connection issues in real-time.
The network administrator types the MAC address of the client device and starts various services to identify the connectivity issue. The APs assigned to the client device relay data frames from the device to the controller which the administrator analysis to determine which stage of the connection is causing problems.
-
Go to
Troubleshooting.
The Troubleshooting page appears.Figure 121 Troubleshooting - Client Connections
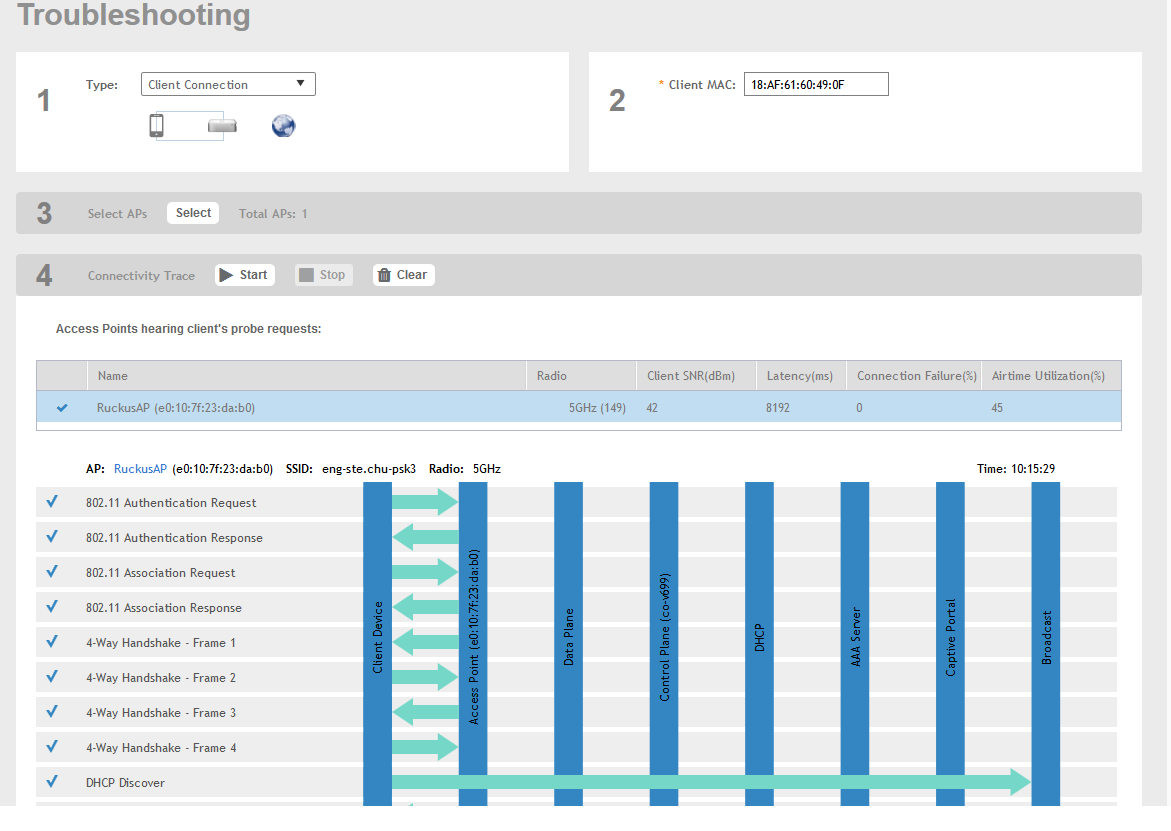
- In Type, select Client Connection from the drop-down menu.
- In Client MAC, type the MAC address of the client device which is facing connectivity issues.
-
In Select APs, click
Select.
The Select APs page appears. Select an AP to communicate between the client and controller and then click OK.
-
In Connectivity Trace, click
Start.
The controller configures the APs to receive data frame from the target client so that the APs can relay relevant frames that match the client filter to the controller.
The APs that receive probe requests from the target client are listed in a table along with the APs operating channel and the RSSI at which the client’s frames were received. This stage of the connection identifies whether there are acceptable APs for the client to connect to.
Following are the details displayed in the table:
- AP Name and MAC Address.
- Radio: Identifies the 2.4 or 5 GHz radio of the AP and the channel number the radio is operating on.
- Client SNR: This is the signal-to-noise ratio received in dB.
- Latency: Time delay in connecting the AP to the client.
- Connection Failures: Displays the percentage of AP-client connection attempts that failed.
- Airtime Utilization: Percentage of the air time that was used by the client to transfer data.
AT this stage, the tool displays the statuses Client is in a discovery state and not currently connected(when the tool starts/when the client is already connected to an AP) and Client is attempting a new connection(when the target client sends an 802.11 authentication request frame to an AP to initiate a connection.).
By using the list of APs that communicated with the client, you will be able to identify if the client chose the best AP based on signal quality and other health metrics.
When the client sends an 802.11 authentication request frame, a flow diagram depicting different stages of the AP-client connection is initiated. This sends a trigger frame to the AP and it is highlighted from the list for reporting APs.
The Flow ladder in the diagram shows the step-by-step exchange of information between devices during the connection process. As the steps are completed, colored arrows are displayed based on whether the step depicts a warnings (yellow) or event (for example, red for failure). Typical warning scenarios include time delays or when a client negotiates and EAP type that's not supported. Failure conditions are also highlighted as red arrows typically when the connection itself fails.
-
Click
Stop to terminate connection between the AP and client.
NOTEThe following authentication types are supported:
- Open
- PSK (WPA2-Personal)
- 802.1X (PEAP, TTLS, TLS, SIM)
- WISPr
