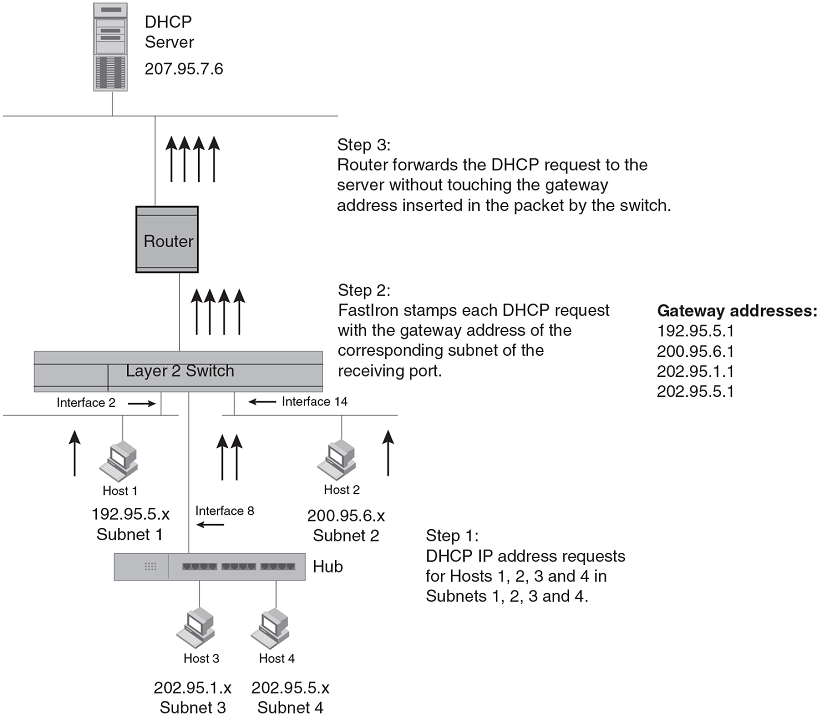
How DHCP Assist works
Upon initiation of a DHCP session, the client sends out a DHCP discovery packet for an address from the DHCP server. When the DHCP discovery packet is received at a Ruckus Layer 2 switch with the DHCP Assist feature enabled, the gateway address configured on the receiving interface is inserted into the packet. This address insertion is also referred to as stamping.
Figure 7
DHCP requests in a network with DHCP Assist operating on a
FastIron switch
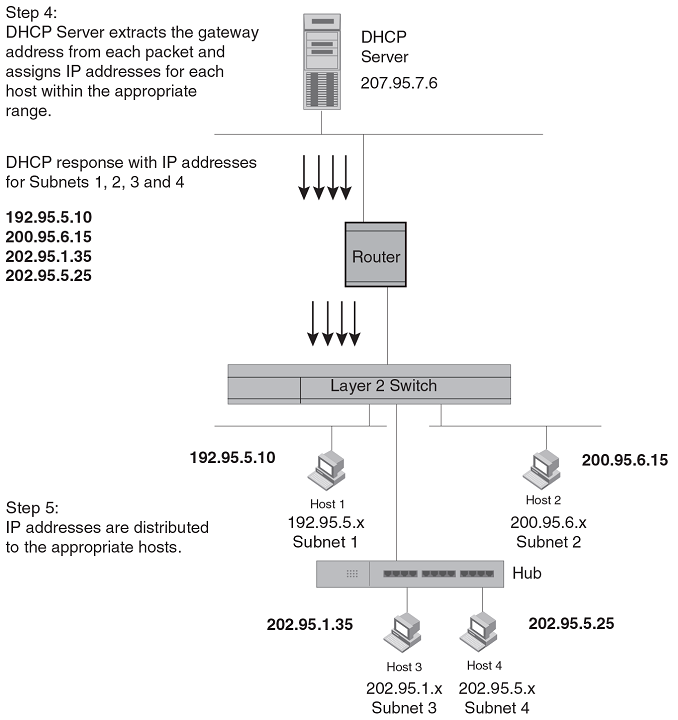
When the stamped DHCP discovery packet is then received at the router, it is forwarded to the DHCP server. The DHCP server then extracts the gateway address from each request and assigns an available IP address within the corresponding IP subnet. The IP address is then forwarded back to the workstation that originated the request.
NOTE
When DHCP Assist is enabled on any port, Layer 2 broadcast packets are forwarded by the CPU. Unknown unicast and multicast packets are still forwarded in hardware, although selective packets such as IGMP, are sent to the CPU for analysis. When DHCP Assist is not enabled, Layer 2 broadcast packets are forwarded in hardware.
NOTE
The DHCP relay function of the connecting router must be turned on.
Figure 8
DHCP offers are forwarded back toward the requesters